What Kind of Disease is COPD?
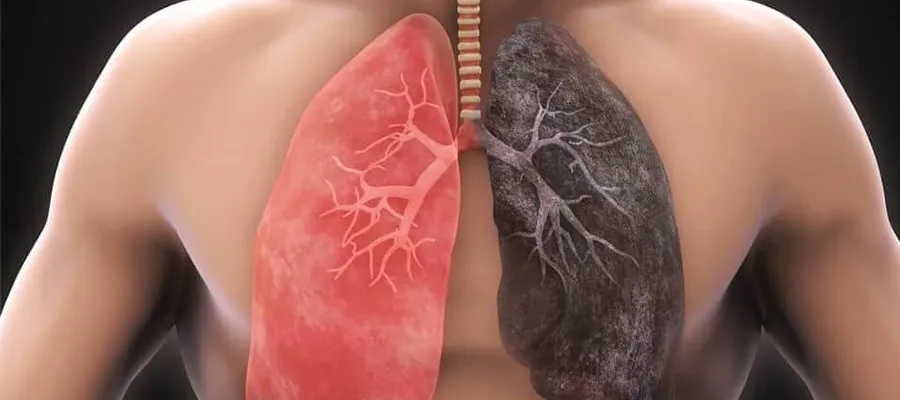
COPD is a chronic and progressive respiratory disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It develops due to various factors, including long-term smoking, exposure to harmful gases, and genetic predisposition. This disease, manifested by symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, and phlegm, can significantly reduce quality of life over time. COPD, which is particularly prevalent in older adults, can be managed with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
COPD is an acronym for “Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.” Conditions such as bronchitis and emphysema, which fall under this group of diseases, are characterized by narrowing of the airways and structural deterioration that impede air exchange within the lungs. The disease typically progresses insidiously, and by the time a person notices symptoms, a significant portion of lung function has been lost.
What Causes COPD?
The most common cause of COPD is smoking. Cigarette smoke triggers the development of the disease by causing inflammation and structural damage to the airways. However, COPD can occur not only in smokers but also in secondhand smokers and workers exposed to harmful chemicals and dust. Using fuels such as coal, wood, and dung in enclosed spaces, in particular, increases the risk of COPD.
Genetic predisposition also plays a significant role. A genetic disorder, particularly alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, can accelerate the development of COPD in some individuals. Furthermore, frequent respiratory infections during childhood can lead to airway deterioration, increasing the risk of COPD later in life.
What are the symptoms of COPD?
COPD symptoms usually develop slowly and initially present with mild symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms become more severe. The most common symptoms of COPD are:
Persistent and chronic cough
Expectoration (especially in the morning)
Increased shortness of breath during exercise
Feeling of tightness in the chest
Wheezing
Fatigue and weakness
These symptoms become more pronounced over time, making daily activities difficult. In advanced stages, a person may have difficulty performing even simple tasks, such as climbing stairs or walking short distances.
How Is COPD Diagnosed?
The most important method for diagnosing COPD is a breathing test called spirometry. This test measures how much air the lungs can inhale and exhale and how quickly they can do so. If the spirometry reveals a decrease in airflow, this is a significant finding in the diagnosis of COPD.
Doctors also inquire about the patient’s medical history, assess smoking habits, and perform a physical examination. If necessary, imaging studies such as a chest X-ray or CT scan may be used. These tests support the diagnosis by revealing structural changes in the lungs.
What are the COPD Treatment Methods?
COPD treatment aims to halt disease progression, relieve symptoms, and improve quality of life. While a complete cure is not possible, the disease can be controlled with appropriate treatment. COPD treatment methods include:
Quitting smoking: It is the most effective and first step treatment.
Inhaled medications: Bronchodilators and corticosteroids that widen the airways are used.
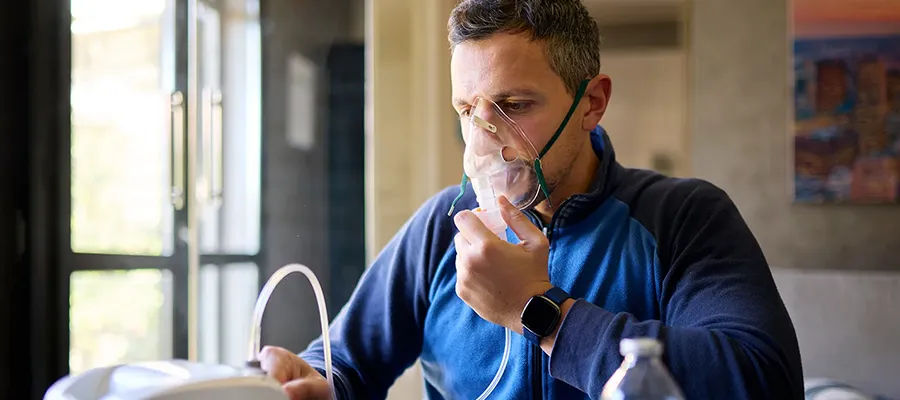
Oxygen therapy: Patients with advanced COPD may require oxygen support at home.
Pulmonary rehabilitation: Programs that strengthen respiratory muscles and increase exercise capacity.
Vaccines: Flu and pneumonia vaccines protect against respiratory infections.
What should be done to prevent COPD?
The most effective way to protect yourself from COPD is to avoid risk factors. Smoking, in particular, is a major trigger for this disease. Furthermore, avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals and air pollution is crucial for a healthy lifestyle.
The following items summarize effective methods for preventing COPD:
Do not smoke and stay away from smoking environments.
Improve the air quality in your home and work environment, do not neglect ventilation.
If you work with harmful gases and chemicals, wear protective equipment.
Monitor your lung function by getting regular health checkups.
Get vaccinated against respiratory infections like flu and pneumonia.
Who is More Affected by COPD?
COPD is generally more common in individuals over the age of 40. The risk is higher in smokers and those whose occupations expose them to dust or chemicals. The prevalence rate is slightly higher in men than in women, although this difference has been decreasing in recent years as smoking rates in women have increased.
Secondhand smoke is also a significant factor that increases the risk of COPD. Even nonsmokers can experience symptoms of this disease when exposed to secondhand smoke for extended periods. Individuals exposed to secondhand smoke, especially during childhood, are more likely to develop COPD later in life.
What are the differences between COPD and Asthma?
COPD and asthma are both chronic diseases that affect the airways. However, there are some key differences. Asthma usually begins in childhood or adolescence and involves sensitivity to allergens. Symptoms are variable and usually completely reversible. COPD, on the other hand, usually appears in older adults, involves irreversible damage, and worsens over time.
Additionally, COPD patients experience more pronounced sputum production and persistent cough. In asthma, these symptoms typically occur during acute attacks. Treatment of these two conditions requires different medications and approaches. With accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment, both conditions can be controlled.
Things to Consider During COPD Treatment
Success in COPD treatment is directly related to the patient’s compliance with lifestyle changes. Regular medication use, avoiding smoking, and a healthy diet are among the most important factors. Exercise and participation in pulmonary rehabilitation programs also improve respiratory capacity.
Patients should also be vigilant against respiratory infections such as colds and the flu. These infections can worsen COPD. Regular checkups with a doctor increase the effectiveness of treatment and help identify potential complications early.
Is COPD Fatal?
Because COPD is a progressive disease, if left uncontrolled, it can lead to serious health problems and even death. However, early diagnosis and effective treatment can slow the progression of the disease and prolong life. Whether COPD is fatal depends on the stage of the disease, the patient’s lifestyle, and their response to treatment.
Serious complications such as heart failure and respiratory failure can develop, especially in patients with advanced COPD. Therefore, it is crucial to be aware of the severity of the disease and take the necessary precautions.
How Much Does COPD Cost?
COPD treatment varies depending on the stage of the disease and the methods used. The medications used, the rehabilitation programs, and the frequency of necessary checkups all influence the total cost. Furthermore, the equipment and expertise of the treating healthcare provider can also determine the cost. Contact us today for COPD pricing.