What is the First Sign of Lung Cancer?
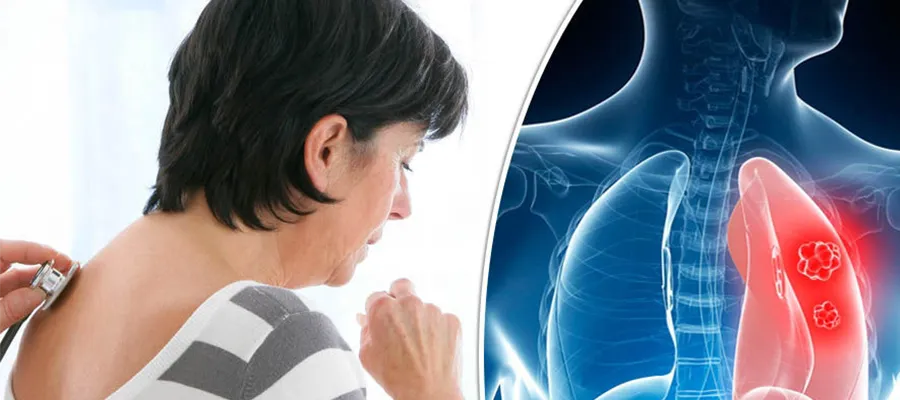
Lung cancer, one of the diseases with the highest mortality rates among cancers today, is often known for its insidious progression. Early diagnosis significantly increases the success rate of treatment. Therefore, the question “What are the first signs of lung cancer?” is vital for both at-risk individuals and healthcare professionals.
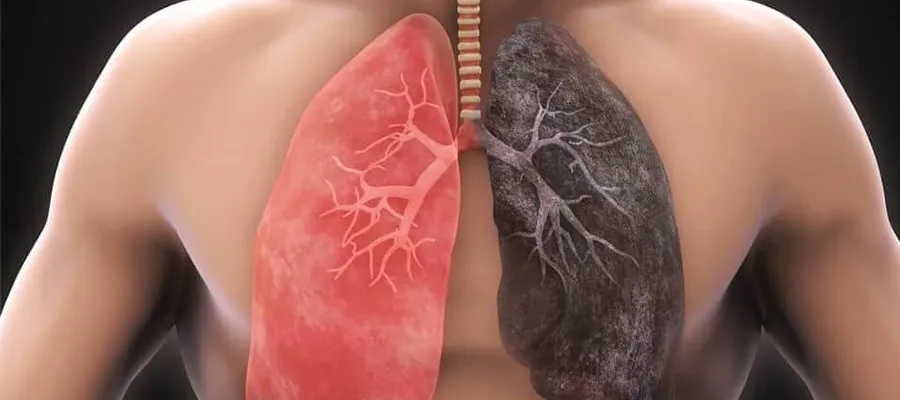
Lung cancer occurs when the cells that make up lung tissue multiply uncontrollably. Over time, these cells can spread to surrounding tissues and other organs. Unfortunately, the disease often progresses without any obvious symptoms. However, some early signs can be detected through careful observation. Not ignoring these symptoms and consulting a specialist promptly can be lifesaving.
The Silent Beginning of Lung Cancer
Many patients with lung cancer experience no symptoms in the early stages. This can lead to delayed diagnosis and the disease being diagnosed in its more advanced stages. Early symptoms are often confused with common ailments like the flu, bronchitis, or a cough caused by smoking. However, these mild symptoms worsen over time and become chronic.
The first symptom of lung cancer can vary depending on where the disease begins, the tumor’s size, and its impact on the airways. However, in most cases, the first symptom is a persistent cough. This cough can last for weeks and worsen over time. Especially in smokers, this symptom can be dismissed as “just smoking,” but consulting a doctor can make a huge difference.
Persistent and Changing Cough
One of the most common and earliest symptoms of lung cancer is a persistent cough. The type of cough a person is accustomed to may change, becoming drier or more phlegmy, for example. The frequency and severity of the cough may also increase over time.
This type of cough is particularly intense in the morning. If the cough persists for more than two weeks and is not a typical symptom, it should be taken seriously. Coughing up blood, in particular, is an even more serious warning sign and requires immediate evaluation.
Shortness of breath
Lung cancer can cause shortness of breath when it blocks the airways or reduces lung capacity. Initially, this shortness of breath may only be felt when climbing stairs or with mild exertion, but over time, it can become noticeable even at rest. This is usually related to the growth of the tumor within the lung tissue.
This symptom should not be ignored, especially if you experience fatigue and air hunger during exercise or daily activities. Shortness of breath can also be caused by other conditions, such as heart disease. However, in individuals at risk, it should be considered one of the first signs of lung cancer.
Chest Pain and Discomfort
Pain, pressure, or discomfort in the chest area can be an early warning sign of lung cancer. This pain usually occurs when the tumor presses on nerve endings or the lining of the lung. The pain can be localized or radiate to the shoulders, upper back, or neck.
A stinging sensation felt when coughing or taking a deep breath can often be dismissed as muscle pain. However, such pain can sometimes indicate that the tumor has spread to surrounding tissues. The duration, severity, and pattern of spread of chest pain must be taken into consideration.
Hoarseness and Voice Changes
When lung cancer presses on the nerves supplying the vocal cords, the patient may experience a change in the voice. If the voice becomes deep, cracked, or significantly hoarse for a long time, it should be evaluated by an otolaryngologist. This symptom is particularly common if the tumor is located in the left main bronchus or upper lung lobe.
Hoarseness isn’t always a sign of cancer; it can also occur due to simpler causes like a cold or infection. However, a voice change lasting longer than a few weeks shouldn’t be ignored, and the underlying cause should be investigated.
Weight Loss and Loss of Appetite
Sudden weight loss without any diet or increased physical activity could be a sign of a problem. Cancer cells rapidly deplete the body’s energy resources, leading to unintentional weight loss. This process may also be accompanied by a loss of appetite.
Such general health issues are rarely noticed as the first symptom of lung cancer. However, when experienced alongside other symptoms, they should be taken into consideration. It is strongly recommended that individuals who experience rapid weight loss over the past few months undergo a medical screening.
Frequent Infections
Recurring lung infections, such as bronchitis or pneumonia, can also be the first signs of lung cancer in some cases. Frequent infections in the same area, in particular, may indicate the development of a tumor in that area. The tumor obstructs the airways, preventing adequate drainage, and this increases the risk of infection.
If you experience two or more serious respiratory infections per year and this hasn’t happened before, the underlying cause should be investigated. This symptom should be particularly important in individuals over the age of 40 who have a history of smoking.
Fatigue and Weakness
Cancer cells consume a significant amount of body energy. This leads to widespread fatigue, weakness, and an increased need for sleep. While waking up feeling rested and feeling exhausted throughout the day are often linked to other causes, in some cases, they can be the first sign of lung cancer.
If chronic fatigue is present, it should be evaluated along with other accompanying symptoms. Further evaluation is necessary, especially if the aforementioned symptoms, such as cough, shortness of breath, or weight loss, are also present.